Iran-Israel Tensions
The Israel-Iran conflict’s immediate impact is heightened oil prices and market volatility, with risks of broader economic disruption if escalation continues. Diplomacy or limited retaliation could stabilize markets, but a wider conflict involving oil infrastructure or the Strait of Hormuz could lead to severe global economic consequences, including inflation, supply chain disruptions, and recession risks. Iran’s weakened proxies, degraded military infrastructure, leadership losses, and economic constraints makes a restrained response more likely than a large-scale counterattack. Should Israel stick to targeting nuclear facilities, it is likely that the conflict remains contained.
US Inflation Easing
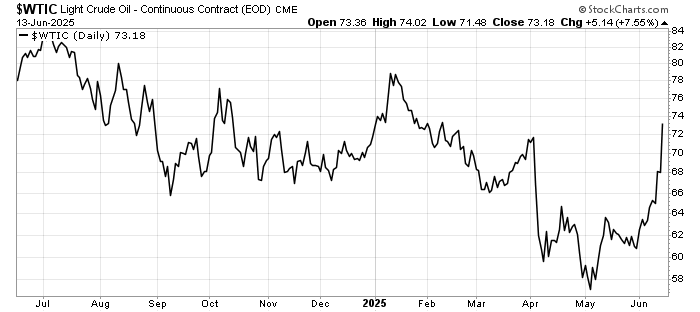
The latest US Consumer Price Index (CPI) report for May 2025 shows inflation rose 0.1% month-over-month, slightly below the expected 0.2%. Over the past 12 months, the CPI increased by 2.4%, matching estimates. Core CPI, excluding food and energy, also rose 0.1% monthly, below the expected 0.3%, with a yearly increase of 2.8%. Shelter and food prices each went up 0.3%, while energy prices dropped 1.0%, driven by lower gasoline costs. This suggests inflation is cooling slightly and tariff concerns have yet to push prices higher. The FED has slightly more room to ease rates.
US-China Trade Truce
The U.S.-China trade truce, agreed upon in London on June 10-11, 2025, is a temporary measure to ease escalating trade tensions. Following a preliminary deal in Geneva in May, this framework seeks to reduce economic friction by scaling back punitive tariffs and restrictions. The U.S. will keep tariffs on Chinese goods at 55%, down from a high of 145%, while China will lower its tariffs on U.S. goods to 10% from 125%. This includes a contested 10% baseline tariff currently under legal review in the U.S. The agreement, however, is limited in scope and awaits final approval from President Donald Trump and Chinese President Xi Jinping, with no guarantee of resolving deeper trade disputes.
As part of the truce, China has committed to loosening export controls on rare earth minerals and magnets, which are vital for U.S. industries like automotive and defense. In exchange, the U.S. will ease restrictions on technology exports and visa limitations for Chinese students. Despite these concessions, the deal is seen as a stopgap, with logistics firms and retailers warning that the 55% U.S. tariff still threatens supply chains, jobs, and businesses. The truce is set to hold until at least July 9, 2025, when a 90-day tariff pause expires, potentially leading to renewed tariff hikes if negotiations falter.
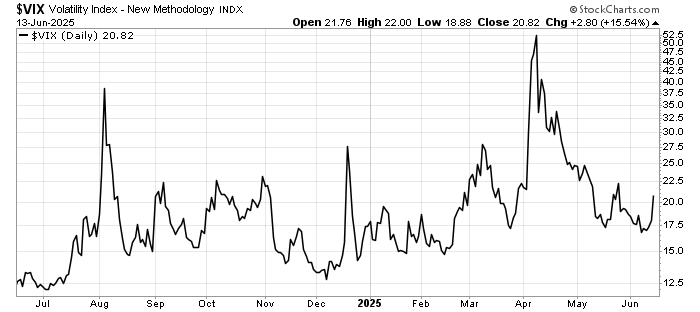
US Stock Market Response To Trade Fading
Since Liberation Day, US stock market volatility has fallen as trade negotiations, legal challenges and Trump’s electorate constraints have limit the impact on investors’ risk appetite. The VIX index has fallen steadily since that fateful day, with lower highs. It would seem that investors are moving on to geo-politics and the inflation/interest rate narratives for the next few quarters.
Leave a Reply