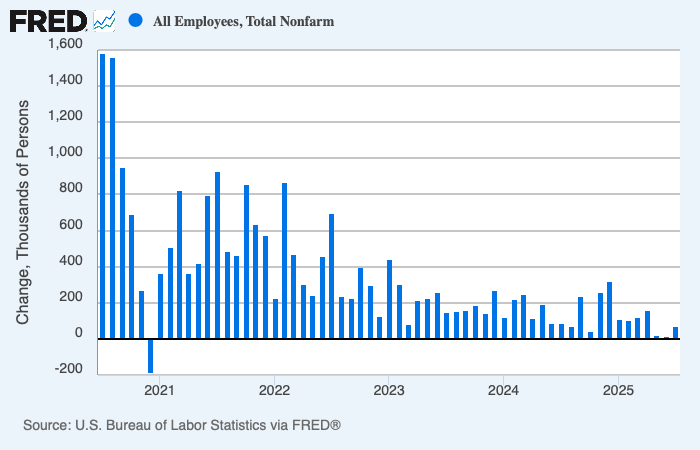
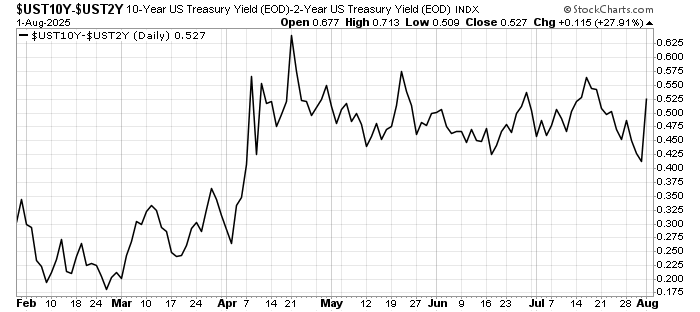
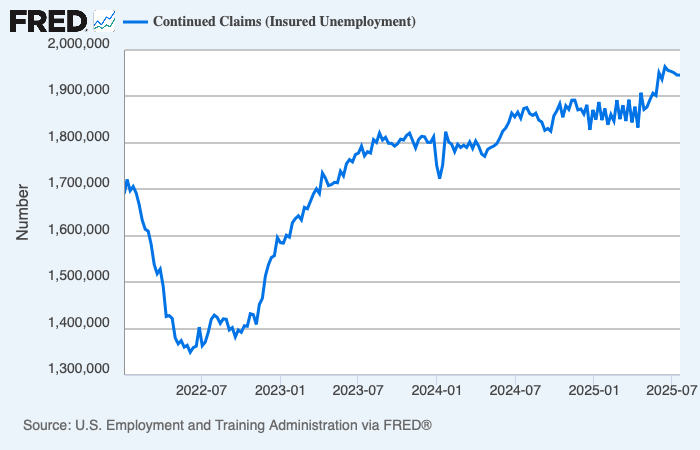
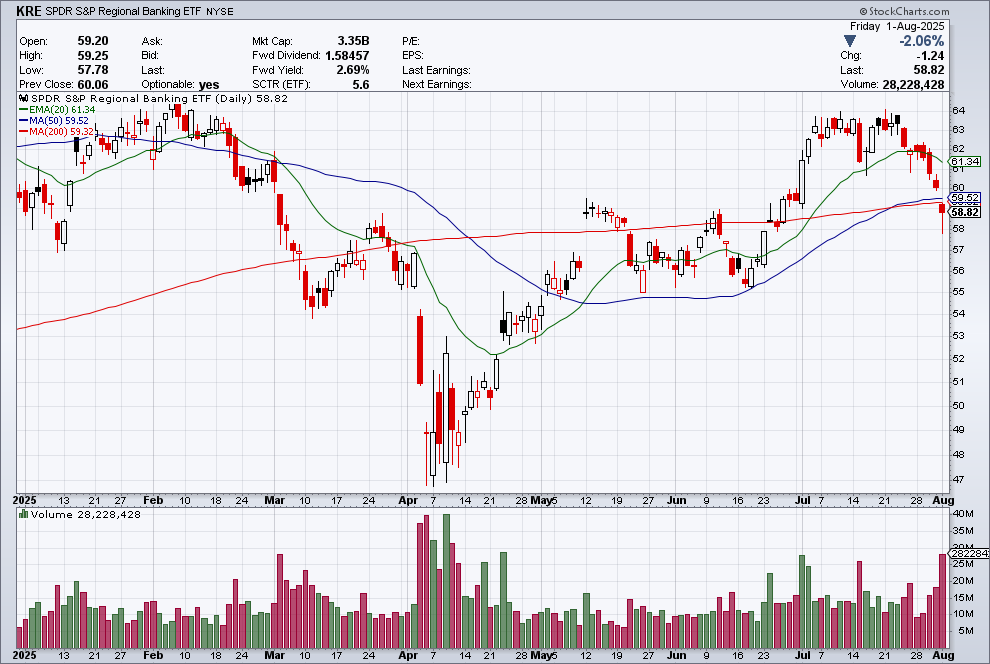
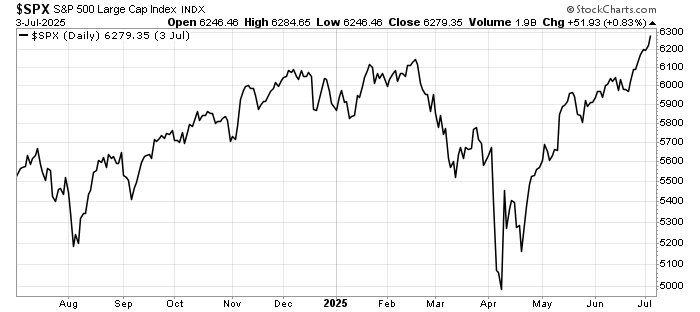
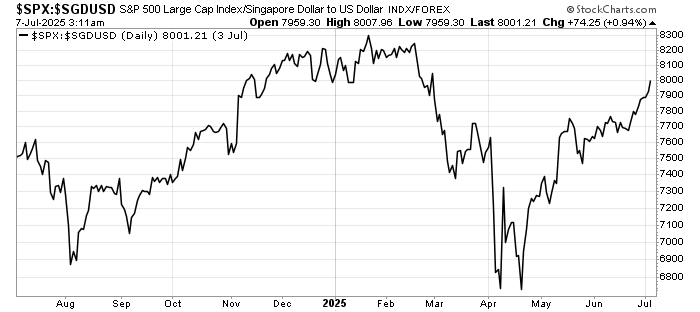
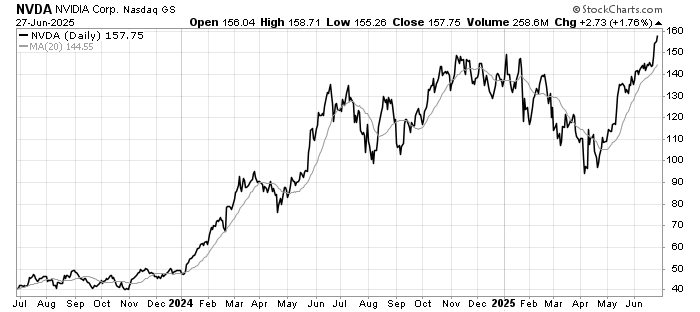
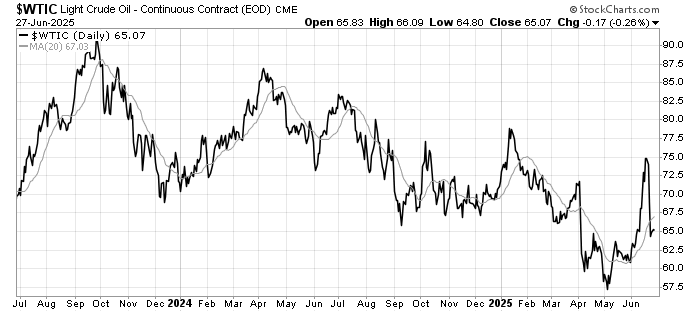
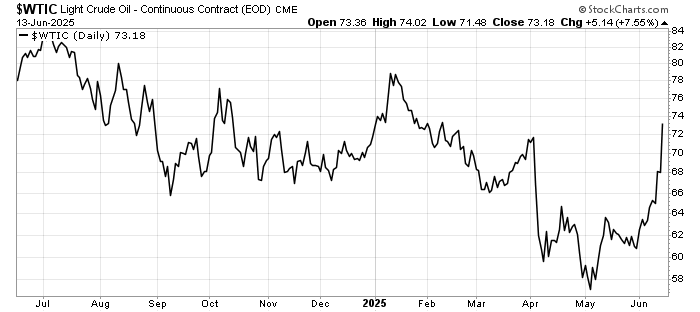
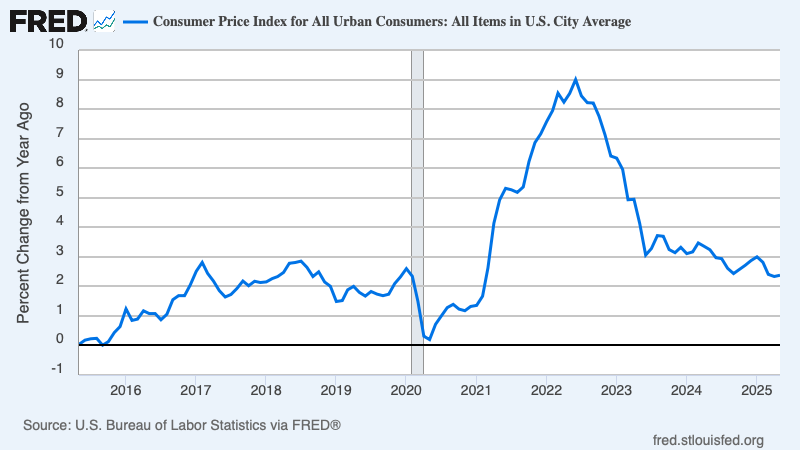
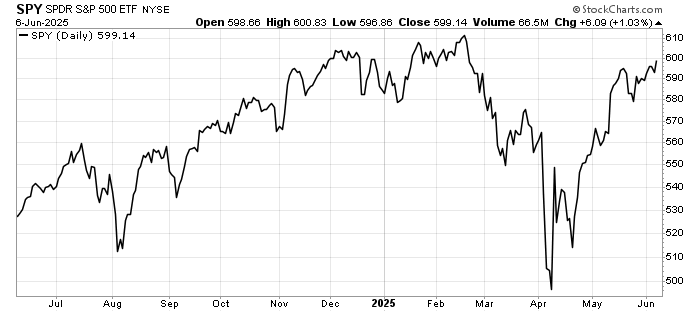
The past week brought three developments that matter greatly to global investors: fresh U.S. inflation data that challenges expectations for monetary easing, a set of weak July figures from China that highlight ongoing fragility in the world’s second-largest economy, and renewed diplomatic engagement between Washington and Moscow over Ukraine.
U.S. Inflation: The Fed’s Job Isn’t Done
The U.S. consumer price index (CPI) for July confirmed what many investors have feared: inflation is not easing as quickly as hoped. While headline CPI edged lower thanks to softer energy prices, core inflation remained stubbornly high, particularly in services and shelter.
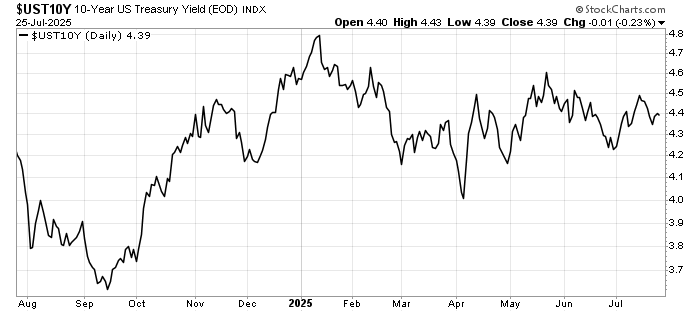
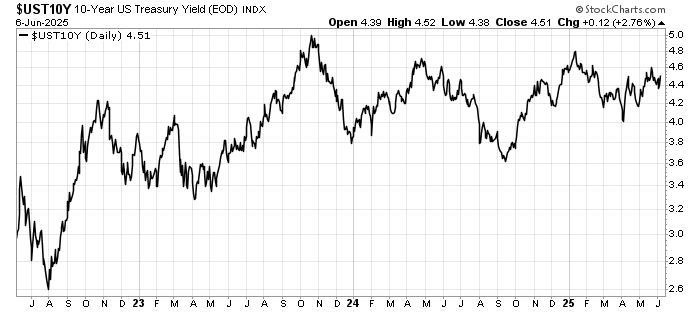
Markets had entered the summer with hopes of multiple Federal Reserve rate cuts before year-end. Those expectations are now being pared back. Futures pricing suggests investors see fewer cuts, later, and at a slower pace than initially anticipated.
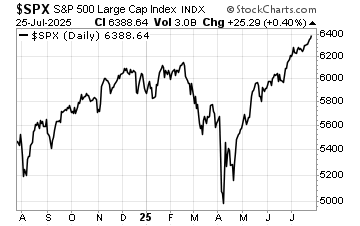
Bond markets reacted immediately. Treasury yields climbed, reflecting the likelihood that policy will remain tighter for longer. Equities wobbled, before regaining some ground later in the week.
The risk of a stagflationary mix—stubborn inflation and slowing growth—is rising. That combination historically favours real assets (gold, commodities) and inflation-linked bonds over traditional fixed income.
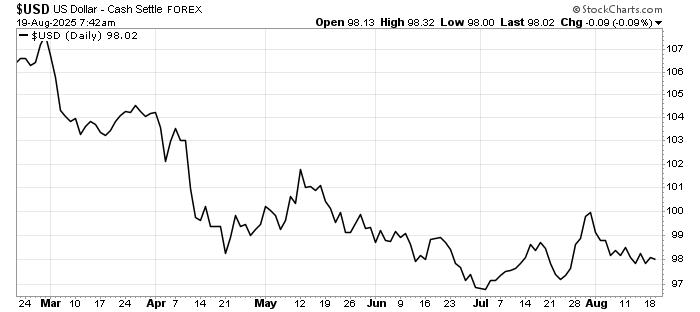
Equities may remain range-bound until markets gain clarity on the Fed’s path. Interestingly, the US Dollar strength remains under pressure despite reasons for the Federal Reserve to hold.
In short, the CPI release reinforces the message that the Fed’s fight against inflation is far from over. Investors should be cautious about positioning portfolios too aggressively for imminent policy easing.
China’s July Data: Momentum Slips Again
China’s July economic numbers painted a disappointing picture. Retail sales slowed, reflecting weak consumer confidence and a still-cautious household sector. Industrial production lost momentum, despite earlier government support measures. Fixed asset investment also cooled, pointing to fading stimulus from infrastructure and property.
Taken together, the data shows that China’s recovery remains uneven and vulnerable. Domestic demand is subdued, exports are struggling against weaker global trade, and the property sector continues to drag on growth.
Markets ignored the weakness, probably looking towards more measures from Beijing. 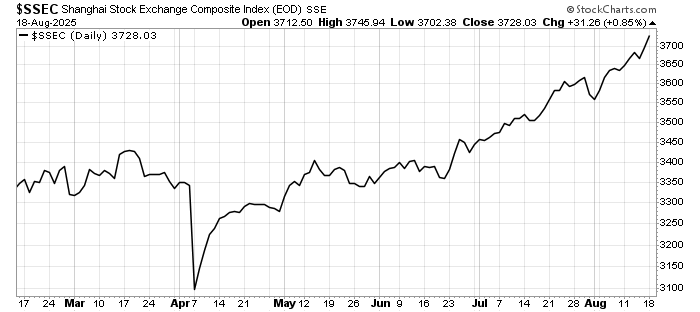
U.S.–Russia Talks: A Glimmer of Diplomacy
In the geopolitical arena, reports confirmed that U.S. and Russian officials engaged in direct discussions over Ukraine. President Trump signalled openness to exploring a negotiated settlement, although no concrete outcomes were announced.
Markets, however, seized on the development as a tentative positive. European equities rallied modestly, with investors hoping that any step toward easing conflict could reduce energy and security risk premiums. Monday’s meeting with Ukraine’s President should be another step towards a three-way meeting that should pave way for a roadmap to a permanent peace in Ukraine.